A gravimetric feeder is a self-calibrating dosing system that doses based on weight in speed.In gravimetric dosing, the weight of the dosed additive is measured using a load cell that is the foundation of the entire system. Weight is calculated using loss-in-weight technology, which measures the reduced weight while dosing. A volumetric feeder is relatively low priced dosing system. Accurate dosing cylinder. Stepper motor speed starting from 0.1 up to 200 rpm. A volumetric feeder, on the other hand, does this based on volume in speed. Extruder Ancillary Machinery,Strand Pelletizer Granulator,Plastic Strand Pelletizer,Plastic Cutter Machine,Paddle Type Mixer JIANGSU XINDA TECH LIMITED , https://www.xindacompounding.com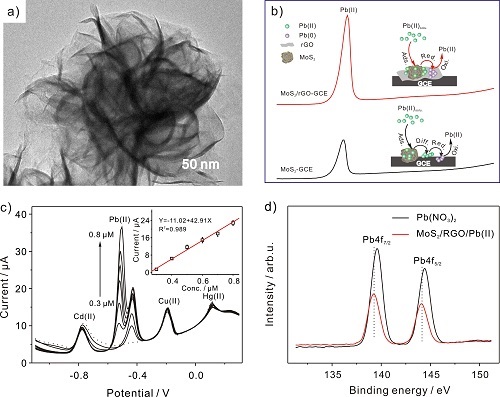
Highly sensitive and highly selective detection of Pb(II) in China has progressed
[ China Instrumentation Network Instrument Development ] Recently, Dr. Yang Meng from the Intelligent Institute successfully developed a highly sensitive and selective method for detecting micro-pollutants such as Pb(II) in water using MoS2/RGO nanocomposites. This groundbreaking research has significant scientific value in achieving accurate and selective detection of heavy metal ions in real-world water samples. The findings were published in the prestigious journal *Analytica Chimica Acta* by Elsevier (2019, DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2019.03.008).
Detecting heavy metal ions through stripping voltammetry often faces challenges due to the formation of intermetallic compounds during the enrichment process. This leads to serious interference when multiple ions are detected simultaneously, making it difficult to accurately identify individual ions. Therefore, developing sensors that can detect specific heavy metals with high sensitivity and selectivity remains a critical challenge in electroanalytical chemistry.
MoS2, a well-known two-dimensional transition metal chalcogenide, has been widely studied, but its application in electrochemical sensing is limited due to a lack of active sites for interaction with heavy metals. To overcome this, researchers combined MoS2 with reduced graphene oxide (RGO), which offers excellent electrical conductivity. This hybrid material significantly enhances the electrochemical activity of MoS2, enabling more efficient detection of heavy metal ions.
The study focused on the anodic stripping voltammetric behavior of heavy metal ions at the MoS2/RGO interface. Results showed that the method provides high sensitivity, selectivity, and resistance to interference, especially for Pb(II). Adsorption experiments revealed that different heavy metals interact differently with the surface of MoS2/RGO. Notably, Pb(II) exhibited much stronger adsorption compared to other ions.
Further analysis using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) confirmed that Pb(II) forms a strong bond with -SOH groups in the MoS2/RGO nanocomposite, contributing to its high adsorption capacity. During the enrichment phase, the increased adsorption of Pb(II) leads to greater deposition of Pb(0) on the electrode. Combined with the excellent conductivity of the modified electrode, this promotes efficient redox reactions, resulting in a stronger electrochemical signal.
The proposed method was tested on wastewater samples from a sewage treatment plant, yielding accurate results and a high recovery rate. These outcomes demonstrate the practical potential of the technique for detecting Pb(II) in real environmental samples.
This research was supported by several key funding programs, including the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Postdoctoral Innovative Talent Support Program, the 13th Five-Year Plan Project of the Hefei Institute of Material Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province.
(Original title: High-sensitivity, high-selectivity, and accurate detection of heavy metal pollutants Pb(II))